Components
1. 4 out 1 in, 3 out 2 in sets.
2. Constantly attacking the rim.
3. Utilizing the 3 point shot as a weapon.
4. Putting tremendous pressure on individual man defense of our opponents.
“1”
- Attack player # 1
- Our main ball handler.
- The catalyst of our attacking offense
- Will be best penetrator/creator
We look to attack at all times.
- Offense is reset. When 2 catches the ball at the top of the key, your players will be reset into the initial formation and ready to run the man-to-man motion again. DIAGRAM 8: Offense is reset. We’ll often try to look for a quick reversal to 5. If 5 is overplayed, he or she can screen down for 4 and pop to the corner.
- #545 Play Wheel Offense (1st & 2nd option) Player 1 passes to 3 who using the two-step rule cuts to the outside. If the ball were on the other side of the floor, the pass would go to 4. Players 1 and 2 scissor the post, with 1 being the first cutter and 2 using 1's pick and 5's screen to brush his man.
- The Blocker Mover Offense made its way to basketball courts when Dick Bennett developed and started using it for his offensive game plan with his teams at University of Wisconsin-Green Bay and again at Washington State University.
- 9 Tom Izzo Michigan State Playbook Half Court Sets Box Flare STS 1 2 3 54 1 passes to 5. Half Court Sets Box Flare STS 1 2 4 3 sets cross screen for 5 and comes off down screen from 4.
“2”
- 2 is the best shooter and will start on the right wing.
- Will run the right lane – Sets up two feet above free throw line extended.
- Is the opposite end @ free throw line extended versus full court pressure.
- “SOB” = Weak-side corner
In play 2, “Iowa Offense”, the ball-side triangle is shown through various actions in the swing offense (up-screen, flare-screen, and shuffle-screen). In the last play, “Izzo”, a wheel action is created as 4 sets a flare-screen as 3 is setting a down-screen. This option gives 5 to cutters for shots.
“3”
- Our second post or biggest guard.
- Runs the left lane – sets up with two feet above free throw line extended.
- Sets up in weak-side corner versus full-court pressure
- SOB = weak side block.
“4”
- Our best offensive post player (catcher and finisher).
- Our best rebounder.
- SPRINTS the floor to the rim.
- Is opposite end of the floor versus pressure.
- Sets up on the left block if does not have anything in transition.
- SOB = ball-side block.
“5”
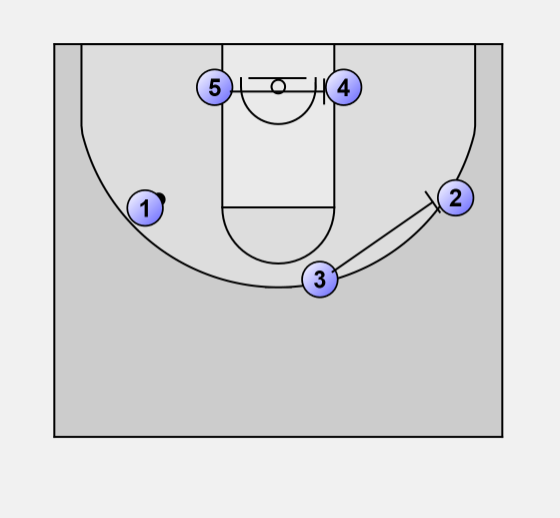
- Our second best ball handler and creator.
- One of our best passers.
- One of our best offensive players.
- Inbounds the ball with speed and trails.
Offensive Rules
1. ATTACK
2. “4 out set 1 in”, the offense will have the right block open on the initial drive.
3. “On a miss” Must fill 4 perimeter spots on a miss, run lanes and be interchangeable.
4. “On a Make” – numbered brake.
5. “Must have a drag man” (Fills behind on penetration – 5 initially)
6. “If Denied” –
• Extend defense – (creates larger gap to penetrate)
• Hard Back Door – (Dribble at = go back door) (Ball Fake = back door)
7. “Opposite Wing Flares on dribble penetration (extend the defense)
8. If there is a dribble to the corner on 4’s side, instant high low.
9. “Divers” create contact off of the dribble –
– “1st Contact” and “Second Contact”
10. Penetrators almost always empty left. “This will result in a wheel action”
11. Never pass the ball to a man inside the three-point line coming away from the basket.
12. Standing and dribbling is not productive unless a great player. Learn to play off the catch.
13. Anytime we a have a player on the block catch the ball = dive the next biggest player on the weak side to the opposite block, as well as the shooter on the weak side making a diagonal cut anticipating a skip.
“4 Set” 4 out 1 in = Wheel
- More of a passing offense.
- Post on the left block. If penetrators break though the shell – no one is home.
- Extended defense = back door.
- Never 2 wings on the right side at the same time.
“3 Set” 3 out 2 in = Kickbacks
- Easier to penetrate ( only three on the perimeter)
- Easier to get 3’s in this offense.
- Look to get the ball in the “Golden Area” at the elbows.
- Strong side post seals on penetrations.
- Opposite wings flare.
- Strong side wing reads defense (loops)
X
- This is when 1 passes to 2 or 5 and instead of cutting though, 1 gives 5 trailing a rub screen to either drive or cut to receive a pass from 2.
2 Game
- This is our stall.
- 3 and 2 will be in the corners instead of a step above free throw line extended.
- 5 and 1 will play keep away up top.
- 4 is always on the block opposite of the ball.
5 Set “Hot”

- This is our 2-1-2 press break.
- Easy – 4 flashes middle.
4 Down
- Isolation for the inside man.
- Stationary on the perimeter, can interchange when next closest is pressured.
- Good against sagging defenses where we can swing or reverse the ball with ease (defense cannot get around in time).
1 ATTACKS – “Penetration Reads for 1”
Rules
1. Pass to the corner = basket cut.
2. 1 to 5, 5 to 1 = X Cut
3. On the X-Cut – cut to the elbow. 5 waits for 1 to get to the elbow before penetrating.
4. On any penetration or pass = 2 players to the corner and 1 player will drag behind.
5. If you want 1 and 5 to be your primary ball handlers = always X cut – this will keep them up top.
6. Options on penetration = get to the rim, wrap around lay-up, kick for 3.
7. On any dribble to the wing = go back door.
8. Sub – 3 minutes on – 1 minute off – 3 minutes on.
9. Always sub 2-3 at a time, never 4.
10. In a 40 minute game = shoot 110 shots.
11. In a 32 minute game = 75 shots.
Offensive Alignments
Wheel = 4 out 1 in
Kickbacks = 3 out 2 in
4 = Spread Offense – delay game
Hot = 2-1-2
5 = 4 out 1 on isolation for the post
2 Game = Stall, 1 and 5 play keep away up top.
13 = 1-3-1 alignment against zone
14 = 4 out 1 in against zone
Box = Zone Set
Spread = Zone Set
Dribble Rules
Crack back = Dribble from the wing to the post area, nearest perimeter player
fills behind.
Loop = Dribble from the top of the key area to the paint/foul
area and the nearest person up top fills behind for the 3.
Drift = Baseline drive, basline drift.
Fade = Drive from the top, wing players fade to the corner.
Opposite = Dribble at a post player, he will always cut opposite.
Go = Dribble at, back door.
Yo Yo = Dribble replace.
Dribble Throw back = Drive in the lane, jump stop, turn and throw behind.
Button Hook = Dribble at a man to post him up.
Flash = Low post player will flash high and we will enter the ball to
the post by using the dribble to improve the angle. (yo,yo)
to circle to post-feed.
Circle = Send the corner man through with an opposite post screen
*Circle with a back screen
circle to post-feed.
Shallow = Dribble replace
Pass Rules
Pass to the wing = Basket cut and fill opposite.
Pass guard to guard = X – cut to the dead spot.
Pass to the post = Dive and split
Sweep = Hand off
Double sweep = 2 Hand offs
Triple sweep = 3 Hand offs
Pass Fake = Back cut
X = Side cut
Smash = Back screen
Post = Basket cut ball screen
Post Feed = Split
Click on the pdf link to download the basketball coaching clinic notes:
Wheel Offense by Anthony Menard
The 5-out motion offense is a fantastic primary offense for basketball teams at any level, but especially youth basketball teams.
It’s a positionless offense that relies on spacing the floor and a set of rules that assists players to determine their movements and actions.
Due to players making decisions and reading the play of their teammates and defenders, the 5-out motion offense is great for teaching players how to play basketball.
Who Should Run the 5-Out Motion Offense?
As a positionless offense, I highly recommend the 5-out motion offense for all youth basketball teams since it allows all players on the team to develop into well-rounded basketball players.
This is important because it’s impossible to know which players will grow in height and which players won’t.
Countless times I’ve seen players who have matured and grown early in life get assigned to the post position only to have their teammates who developed at a later time quickly catch up to them.
When this happens the player who developed early has had barely any practice at dribbling, shooting from the outside, etc.
So it’s imperative that all youth coaches use a positionless offense like the 5-out motion offense.
But with that said (sorry for the rant), it’s especially a great offense for teams that lack height and want to run a fast offense with a lot of movement.
Strengths:
• Creates positionless players – All 5 players on the court are required to pass, cut, dribble, shoot, screen, etc. This is imperative for a great youth basketball offense.
• Can be used as a delay offense – If your league doesn’t have a shot clock and you want to hold up the basketball, the 5-out motion offense will provide movement and keep the defense honest while not looking at scoring options.
• Players learn how to play basketball – Don’t overlook this benefit. Players learn to read their teammates and defenders and make decisions accordingly. This is an important process that players won’t learn from running set plays all game.
• Every player contributes – When running this offense, one or two players can’t dominate the basketball. All players will be involved and must contribute to the team’s offense.
• Requires great spacing – If players are all in the correct positions, your team will always have great spacing at all times. This opens up driving lanes and makes it difficult for defenders to help each other.
• Difficult for opposition teams to scout – Since there are no ‘set’ passes or actions, teams won’t be able to work out a specific action they can stop to disrupt the offense.
• The opposition can’t crowd the key area – All defenders on the opposition team will be required to guard all areas of the floor. This prevents them from keeping their biggest players on the inside.
• Easy to teach due to progressions – One of the best things about the 5 out motion offense is that it can be taught in progressions. Players aren’t forced to learn the complete offense all at once which will overwhelm them.
Weaknesses:
• Not great for teams with one dominant player – If you have one or two dominant players that contribute the bulk of your team’s scoring, this might not be the offense for you if you want your team to continue to play that way. All players must contribute in the 5 out offense. Even the weaker players.
• Players can get stuck in the motions of the offense – When you first implement this offense with your team, you’ll find that they’re so focused on running the offense properly, that they forget to look for scoring opportunities.
• Sometimes difficult with a shot clock – Similarly to the above point, if your players aren’t constantly searching for scoring opportunities, the shot clock can play a factor and force your team to rush a shot with a few seconds left.
• Can take some time for players to master – While your players can quickly pick up the actions and movements of the 5 out, it does take time for players to learn how to quickly read the game and make smart decisions on the court.
5 Out Motion Rules
The 5 out motion offense is governed by 5 rules that players must follow at all times for the offense to run smoothly.
1. If your being denied and the player with the ball looks at you, back cut immediately – Never hesitate. This assumes you’re only being denied one pass away from the basketball.
2. If you believe you can attack the basket and score on your defender, do it – Players must understand their own abilities and the abilities of their defender. If a player thinks they can attack, they should do it immediately on the catch.
3. Players must square up to the rim when they have the basketball – A player can’t telegraph what they’re going to do by facing a certain direction. By squaring up, players can shoot, pass, or dribble.
4. Every action must be performed with purpose – If you cut, cut hard. If you’re screening, focus on setting a great screen. Never pass and stand still.
5. Spacing is always on the NBA three-point line – The NBA three-point line is about 2 feet behind the normal three-point line.
Setting Up the 5 Out Motion Offense
‘5 out’ simply means that all offensive players on the floor are starting outside the three-point line.
There are 5 spots that must always be filled unless players are performing an action like screening or cutting.
The five spots are:
1. Left corner
2. Left wing
3. Top
4. Right wing
5. Right corner
These spots should be on the NBA three-point line which is about 2 feet behind the regular three-point line used by all other levels.
When teaching the 5-out motion offense to your team for the first time, I highly recommend you use cones to mark these 5 spots on the floor to allow players to get used to where each position is.
How to Run the 5-Out Motion Offense
There are 4 progressions that you gradually introduce one by one into the continuity of your 5-out motion offense.
All coaches must make sure they start with progression one and move up without skipping steps.
This allows the players to gradually learn the concepts of the 5-out motion offense without being overwhelmed with the entire offense all at once.
These are the 4 progressions:
Progression 1: Basic cutting
Progression 2: Screening away
Progression 3: On-ball screen
Progression 4: Dribble at
Let’s go through each of the progressions in more detail…
Progression #1 – Basic Cutting
The easiest way to begin teaching your team the 5-out offense is to start with the basic movements of passing and cutting in a 5-0 situation.
Start by setting out 5 cones at the 5 fill spots on the court. Let your team know that when they’re not cutting, they must be in one of these 5 positions.
Now it’s time to teach the cuts…
There are 4 passes and cuts that can be made during progression 1.
1. Top to Wing Pass
On a top to wing pass, the passer basket cuts all the way through the key and fills the opposite corner.
Once 1 has cut, 3 and 5 must fill up the positions closer to the basketball.
2. Wing to Corner Pass
On a wing to corner pass, the passer also basket cuts all the way through the key and fills the opposite corner.
Once 2 has cut through, 3, 5, and 1 must all fill up the positions closer to the basketball.
3. Corner to Wing Pass
On a corner to wing pass, the passer basket cuts and replaces themselves.
The other 4 players wait in the same spot for the next action.
4. Wing to Top Pass

On a wing to top pass, the passer basket cuts and then fills the corner of the same side they cut from.
On 3’s cut, 4 fills up closer to the basketball and then 3 replaces them in the corner. The other 3 players wait for the next action.
Progression Practice:
Have your players practice this progression until they’re comfortable with the passes and cuts.
This simple progression can be a great offense for a youth basketball team by itself. It will provide great spacing and get your players reading the play and making decisions.
Coaching points when teaching progression #1:
• Remind your players that if they’re being overplayed, they must back cut immediately when the player with the basketball is looking at them.
• To set up the defender and get open on a front cut, after passing the player should take one step away from the ball and then explode to the ball-side of their defender on the cut to the rim looking for the basketball.
• If the defender ‘jumps to the basketball’ taking away the front cut, the passer should back cut and try to step in front of their defender to open up the passing angle.
• Always watch the basketball on cuts. If a shot is put up, they need to know immediately to establish rebounding position.
• Cut hard on all cuts to the rim. Doing so will make the cutter a threat to score which will force weak side defense to help.
Progression #2 – Screen Away
Once your team is comfortable with the cutting phase (making the correct cut 80% – 90% of the time), it’s time to introduce the action of screening away after a pass instead of cutting.
This action can be performed on any top to wing, wing to corner, or wing to top pass. The only pass it can’t be performed on is the corner to wing pass.
Before implementing this action, you must decide whether you want the player being screened to always curl, or whether you’ll give them the option of cutting to the top or curling.
I recommend all youth basketball teams (below high school) get this player to curl off the screen every time so that there’s no confusion.
For high school teams and higher, you can allow them to read the defense and perform the most appropriate option.
Option 1 – Screened player always curls off the screen
Here’s how it works on a top to wing pass…
1. 1 makes the pass to 2 on the wing. Instead of cutting, 1 decides to set an away screen.
Note – It’s important that 2 waits while this screen is being set so that the curling option is not missed due to passing to 4 too quickly.
2. 1 screens for 3 making sure that they set the screen at an angle that allows the 3 to cut to the rim.
3. 3 can either front cut or back cut towards the rim depending on how quickly the defense reacts to the screen. But they must cut to the rim since they were screened.
4. After 3 has used the screen, 1 pops back out to the same spot that they set a screen from. If 1’s defender attempts to help on the cut from 3, you’ll find that 1 will often get an open shot from the top of the key.
5. After the cut, 3 fills the weakside corner position since 5 has filled 3’s previous position on the wing.
Then all players are back in position for the next action to be made.
Option 2 – Screened player has the choice of curling or popping out
If you’re coaching an experienced basketball team, you can give the player being screened the option to curl or to pop out to the perimeter and receive the pass.
The difference when using this option is that the screener must go the opposite direction to the cutter.
If the cutter decides to pop out to the perimeter, the screener will cut to the rim and then fill the corner.
If the cutter decides to curl, the screener will pop out to their original position.
Here’s an example of a top to wing pass using option 2…
1.1 makes the pass to 2 on the wing. Instead of cutting, 1 decides to set an away screen.
Note – It’s important that 2 waits while this screen is being set so that the curling option is not missed due to passing to 4 too quickly.
2. 1 screens for 3 making sure that they set the screen at an angle that allows the 3 to cut to the rim.
3. 3’s defender cheats and goes under the screen so 3 pops out to the top perimeter position to catch and look for the open shot.
4. Reading this, 1 cuts to the rim because they must go the opposite direction of the cutter.
5. 1 then fills the corner position as 5 has filled 3’s previous spot on the wing.
I’ve found that inexperienced teams can struggle with option 2 so I recommend starting with option 1 and then progressing to option 2 if you think your players are capable.
Coaching points when teaching progression #2:
• Players must be setting screens on the correct angle. This means the screener’s bum should be facing somewhere between the player with the basketball or the basket. Too often youth players will set screens too high that allow the defender to quickly slip under it.
• The player setting the screen must make the player being screened aware with a verbal cue and a visual sign. I recommend you teach the screener to hold their arm up in a fist and call out the player’s name before setting the screen.
Progression #3 – On-Ball Screen
Once your players are comfortable with cutting and screening away, next up is the action of setting on-ball screens.
This action of the pick and roll is often very effective because the offensive players are spaced out well.
The on-ball screen can be used after any pass in the offense.
Here are two examples of setting an on-ball screen in the 5-out motion offense:
Example #1 – Top to Wing Pass On-Ball Screen
1. 1 passes from the top to 2 on the wing and then sets an on-ball screen on their defender.
2. 2 uses the on-ball screen and drives hard to the rim surveying the options that are presented.
3. Depending on how the defense reacts, 2 can pass to any of the perimeter players or make the shot in the key.
If the basketball is kicked out and the shot isn’t immediately taken, all players must find one of the 5 fill spots and the 5-out motion offense starts again.
Example #2 – Wing to Corner Pass On-Ball Screen
1. 4 passes to 2 in the corner and then sets an on-ball screen on their defender.
2. 2 uses the on-ball screen and drives hard to the rim surveying the options that are presented.
3. Depending on how the defense reacts, 2 can pass to any of the perimeter players or make the shot in the key.
A lot of coaches who run the 5-out motion offense make it a rule that on each pass to the corner the passer sets an on-ball screen. So if it works for you, consider incorporating it as a rule into your offense!
Coaching points when teaching progression #3:
• As with the previous progression, it’s super important that players are setting the on-ball screen at the correct angle that allows the player with the basketball to attack the rim.
• The three players not involved in the pick and roll should do their best to move into open positions where they can catch and shoot or catch and drive.
• Start to introduce to the players that they must take into account each player’s skill set before making an action. For example. Your team should not set an on-ball screen for player that can’t dribble the basketball well.
• Just like in the screening away progression, players must be giving a visual and verbal cue to the player they’re about to set an on-ball screen for by saying their name and holding up a fist.

Progression #4 – Dribble At
Another action to add to this continuity offense is the ‘dribble at’ action.
This can be used when a player with the basketball is being heavily pressured and the only options to pass are being denied well by the off-ball defenders.
In this scenario, the player with the basketball may decide to dribble towards another player at a different spot.
When this happens, the two offensive players involved (the dribbler and the player they’re dribbling towards) have two options.
1. Backcut
If the player without the basketball is being denied, they can make a hard back cut looking to receive the basketball for a layup.
If they don’t receive the pass, they fill the weakside corner, the other players rotate towards the basketball, and the next action begins.
2. Hand-off
The other option is to perform a hand-off between the two players.
This is similar to the pick and roll where the other 3 players on the court should hold their positions and wait.
The player that receives the hand-off should attack the rim and kick out to shooters if the defense slides over to help.
Coaching points when teaching progression #4:
• When performing hand-offs, the player with the basketball should rotate their hands so that they’re on the top and bottom of the basketball. This allows the player receiving the hand-off to grab the basketball on the sides.
• In my opinion, I don’t like hand-offs for youth basketball. For my youth teams, I have them automatically back cut on a dribble at.
Piecing the 5-Out Motion Offense Together
Once your players have learned the basic 4 progressions of 5-out motion offense, you’ve established a fantastic primary offense that will teach them how to read and play the game of basketball.
Now that they can confidently perform all the actions, the next important step is for players to work out what actions work the best for them and their teammates.
For example:
• Players will work out that the best players to set on-ball screens for are the quick guards who make great decisions.
• The best players to away screen for are those that cut hard to the rim and can finish the layup or close shot.
• The bet shooters on the team should primarily set away screens so that they’re cutting back out to the basketball for the open shot.
While a lot of this knowledge will develop with experience, I believe it’s important for the coach to talk to the team and each player individually about what they’re good at and what they need to improve on.
Doing so will help their decisions when running the 5-out motion offense during the game.
Advanced
Flex Action Progression
Once your team has mastered the basic progressions of the 5-out motion offense, you can choose to add a more advanced flex cut progression.
This is best used on a pass from the wing to the top of the key and can potentially give you an open layup off the flex cut or an open jump shot off a down screen.
Here’s how it works:
Basketball Wheel Offense Pdf Example
1. 2 makes the pass to 1 at the top of the key.
2. After making the pass, 2 will basket cut as usual. But instead of filling to the same side, 2 sets a flex screen for 5.
3. 5 uses the flex screen and cuts through looking to receive the pass for the layup. If 5 isn’t open, they simply cut all the way through to the corner as 4 has moved up the wing to replace 2’s spot.
4. 3 then sets a down screen for 2.
5. 2 uses the down screen and pops out to the perimeter looking to receive the basketball for the jump shot.
6. 3 can reverse pivot and seal 2’s defender if they have a mismatch inside. If not, 3 fills the closest corner.
Even if the offense doesn’t get a great look from the flex option, you will notice now that all five spots are now filled and the team can move on to the next action of the offense.
Variation – Cutting Through the Nail
Another variation of this offense I wanted to share with you is the option to ‘cut through the nail’ every time a player cuts to the top of the key.
This is most commonly seen in Bob Huggins’ Open Post Motion offense.
Instead of filling to the top spot just like any of the other 4 spots, players are required to L-cut through the nail.
Note – The ‘nail’ is the spot at the very middle of the free-throw line.
When players cut through the nail, they’re required to decided whether to back cut or to pop out to the top spot depending on how their defender is playing them.
If the defender is denying them from receiving the basketball, the player must immediately back cut and then fill the weak side corner.
If the defender is playing off them, the player cuts out to the top spot to receive the pass.
Basketball Wheel Offense Pdf Free
By implementing this variation to the 5-out motion offense you will achieve two things…
1. It will take away the defenders ability to get a deflection which leads to the opponent’s fast break.
2. It can lead to some easy scores off the back cuts.
Getting the Basketball to the Post
The best way to get the basketball inside to players who have a mismatch is to allow those players to establish quick post up position after every through the key.
The player posting up is only allowed to hold this position for 1 – 2 seconds before clearing out if they don’t receive the pass.
This ensures that the 5-out motion offense continues to run smoothly.
Basketball Wheel Offense Pdf Template
To take advantage of this mismatch, it’s important that players with the basketball are looking at cutters to take advantage of the 1 – 2 seconds that they secure inside position.
Posting up isn’t restricted to your biggest players. Any match up on the floor with an advantage in the post can use this technique.
Transition Defense and Rebounding
One thing a lot of coaches will find confusing is that since all our players are standing outside the three-point line, who’s going to rebound!?
The answer to this question will depend more on the personnel on your team and how aggressive you want to be rebounding the basketball.
I’ll give you three options. Pick the one you like the most depending on your coaching style and players on your team.
1. The point guard always plays safety. The other four players crash the boards.
2. The point guard and shooting guard always play safety. The other three players crash the boards.
3. Everyone below the free throw line rebounds. Everyone above the free throw line plays safety.
What you’ll quickly realize is that the 5-out motion offense can lead to a lot of offensive rebounds as long as your designated players are willing to work hard for them.
By starting on the perimeter when a shot is put up, it’s incredibly difficult for the defense to box out an offensive player with a running start.
If you have any tough and athletic players on your team, expect them to grab a lot of offensive rebounds!
Conclusion
The 5-out motion offense is a great offense for any basketball coach to learn and implement with their team.
Being a very common offense, even if you don’t use it with your own team, it’s important for all coaches to learn about so that they know how to defend when playing against it.
Wheel Offense Basketball Pdf
It allows players to practice all skills, gets the whole team involved, and can be easy to teach as long as you’re using the right progressions and not trying to implement the whole offense at once.
Wheel Offense In Basketball
Any basketball coach who uses this offense will know they’re improving their players!